人脸识别欺骗方式主要包含如下三种:
- print attack
- replay/video attack
- 3D mask attack
Dataset
| Dataset | # subj. / # sess. | Links | Year | Spoof attacks | Publish Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NUAA | 15/3 | Link | 2010 | 2010 | |
| CASIA-MFSD | 50/3 | Link | 2012 | Print, Replay | 2012 |
| Replay-Attack | 50/1 | Link | 2012 | Print, 2 Replay | 2012 |
| MSU-MFSD | 35/1 | Link | 2015 | Print, 2 Replay | 2015 |
| MSU-USSA | 1140/1 | Link | 2016 | 2 Print, 6 Replay | 2016 |
| Oulu-NPU | 55/3 | Link | 2017 | 2 Print, 6 Replay | 2017 |
| SiW | 165/4 | Link | 2018 | 2 Print, 4 Replay | 2018 |
| ROSE-Youtu | 25/* | Link | 2018 | Print, Replay, Mask | 2018 |
Details:
- NUAA: 包含 12641 静态图片;
- CASIA: 包含 50 个对象共 600 视频, 覆盖三种攻击方式 (photo, cut photo, video). 对于每个对象, 真实人脸和三种攻击方式捕获的人脸包含了三种不同图像质量的人脸 (低, 正常, 高);
- Replay-Attack Dataset: 包含 50 个对象共 1300 视频. 对于每个对象, 有两种拍摄背景 (control and adverse), 三种攻击方式 (print, digital photo and video), 两种攻击形式 (fixed and hand-holding).
- MSU_USSA: http://biometrics.cse.msu.edu/Publications/Databases/MSU_USSA/
- Oulu-NPU: 包含 4950 个真实和攻击视频. 采集设备包含 (Samsung Galaxy S6 edge, HTC Desire EYE, MEIZU X5, ASUS Zenfone Selfie, Sony XPERIA C5 Ultra Dual and OPPO N3).
- SiW: 共 165 个对象的视频. 每个对象包含 8 个活体和 20 个欺骗视频. 一共 4478 个视频. 每个视频 30 fps, 持续 15 秒, 1080P HD. 活体视频包含了不同的距离, 姿态, 光照和表情. 欺骗视频包含了打印纸张和翻拍.
- ROSE-Youtu: 包含 25 个对象, 共 4225 个视频 (3350 videos with 20 subjects publically available with 5.45GB in size). 每个对象包含 150~200 个视频片段, 每个片段约 10 秒. 数据来源: Hasee, HUAWEI, ipad 4, iphone 5s, ZTE. 人脸到相机距离 30~50 cm.
Methods
Introduction
Texture-based
- hand-crafted features: LBP, HoG, SIFT, SURF et.al.
- classifers: SVM or LDA et.al.
- overcome illmulation variation: using HSV and YCbCr domain color space, Fouriers spectrum.
- Deficiency: easily fooled by HD screens
Temporal-based
- temporal cues: eye-blinking, motion of mouth and lip
- cons: only for paper attack.
- frame concatanation: Haralick features, motion mag, LSTM-CNN
- birnary classfication, hard to cross-database testing
Motion-based
- eyes blinking
- analyse motion correlation efficient between face region and background
- LBP-TOP, LDP-TOP, DoG
- DMD(dynamic mode decomposition)
- Deficiency: easily fooled by replayed video
Hardware-basd
- multi-spectral cameras, depth cameras, light-field cameras.
- Deficiency: devices limited useage, NIR and depth camera are not stable enough in sunlight.
rPPG
- eliminate the specular reflection by color difference, and estimate two orthogonal chrominance signals
- estimate rPPG from 3 face regions and 2 non-face regions
趋势: 多模态融合
Performance
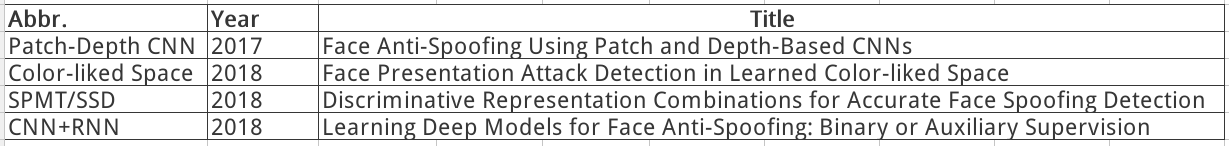
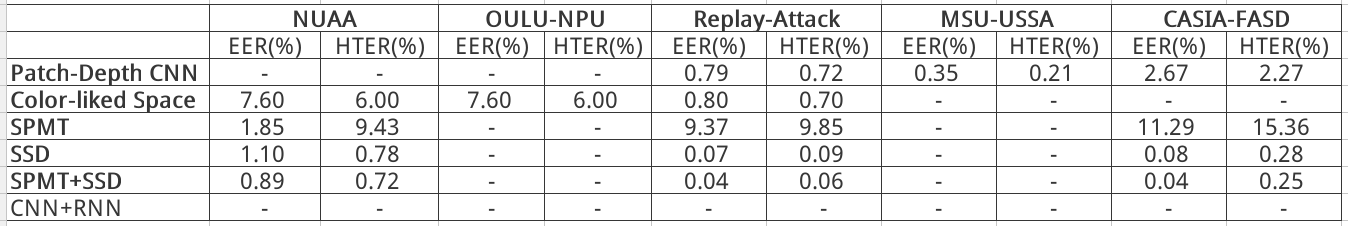
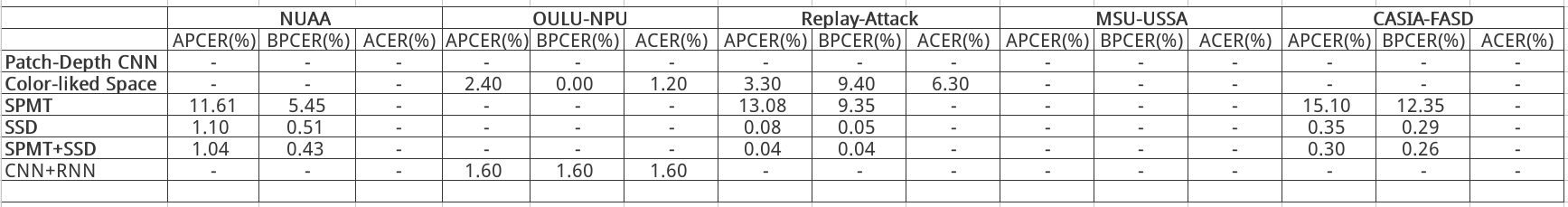
Discriminative Representation Combinations for Accurate Face Spoofing Detection (2018)
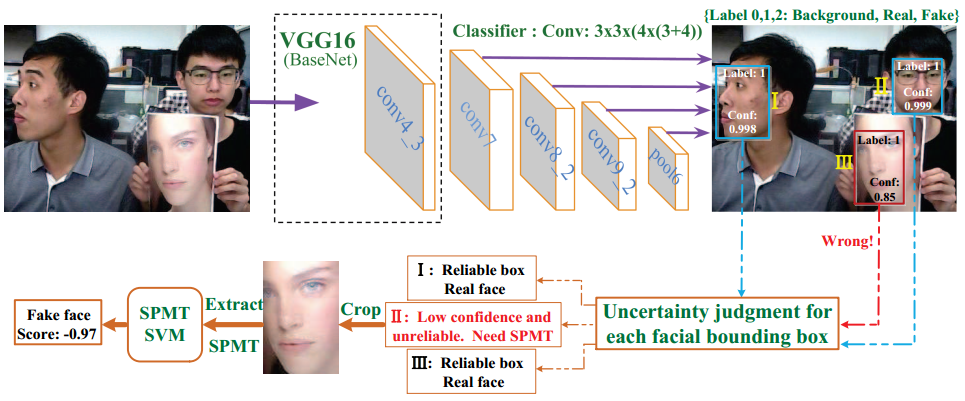
关键词:
SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector
SPMT: 空间金字塔编码的微纹理特征 (spatial pyramid coding micro-texture)
TFBD: 模板人脸匹配的深度特征 (template face matched binocular depth)
思路
- 全画幅图像 → SSD, 判别容易样本
- 难区分样本 → 提取 SPMT 特征, 进一步使用 SVM 鉴别
- 双目图像对 → 提取 TFBD 特征. 需数轮反复迭代.
方法分析
整个方法采用级联思路, 先经过 SSD 网络, 后续对难样本使用手工特征分类. 从结果上看, 该方法有效的根本原因在于 SSD. SPMT 和 TFBD 手工特征计算量大, 方法复杂, 且提升性能有限.
SSD 能够有效区分活体和欺诈样本的原因有二:
- 全画幅输入, 提供了拍摄背景信息;
- SSD 深层和浅层特征融合, 有效提取了纹理特征和结构信息;
改进方向
- 是否有必要全保留 SSD 整个检测结构?
(1) 我们已经有了 MTCNN 做人脸检测, SSD 再检测一遍人脸略显多余;
(2) SSD 需要回归人脸边框, 增加了网络优化难度. 当然, 从多任务角度来讲, 也可能起帮助作用 ? 待验证.
(3) SSD 的输入图片需要缩放到固定尺寸, 容易损失人脸的微纹理信息. - 是否有必要全画幅输入?
SSD 有效的原因之一是利用人脸的背景信息, 全画幅的背景信息是否多余? 能够在 MTCNN 检测人脸的基础上向外多扩展一些边框以提供足够的边缘信息.
Face Presentation Attack Detection in Learned Color-liked Space (2018)
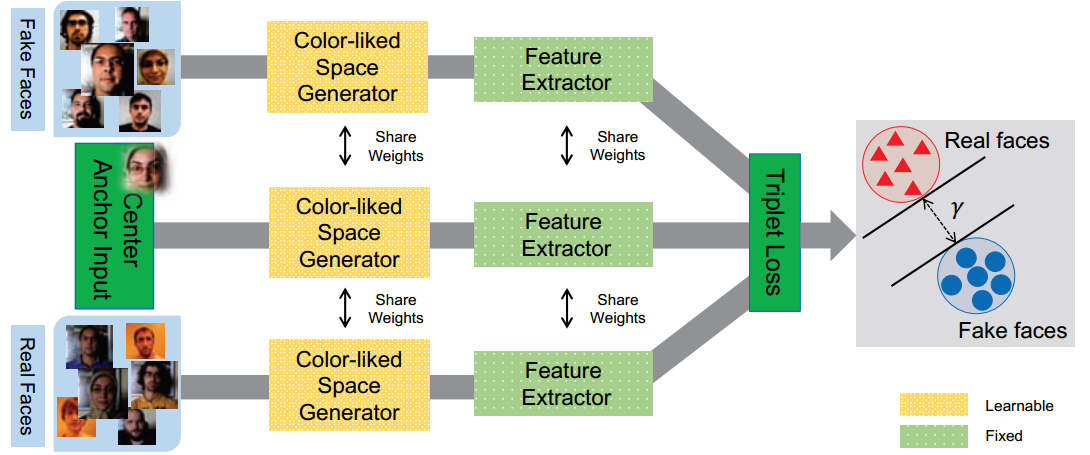
本文一改传统方法在固定的颜色空间 (RGB, HSV, YCbCr) 提取特征然后分类, 通过设计 end-to-end 的网络学习便于区分活体与非活体的颜色空间. 提出的网络包含一个色彩空间生成器和一个特征提取器. 训练的损失函数采用了 Triplet Loss.
有两个风险: 一是生成器结构较大, 实时性难保证; 二是 Triplet Loss 相关损失函数难训练, 调参难度高.
Learning Deep Models for Face Anti-Spoofing: Binary or Auxiliary Supervision (2018CVPR)
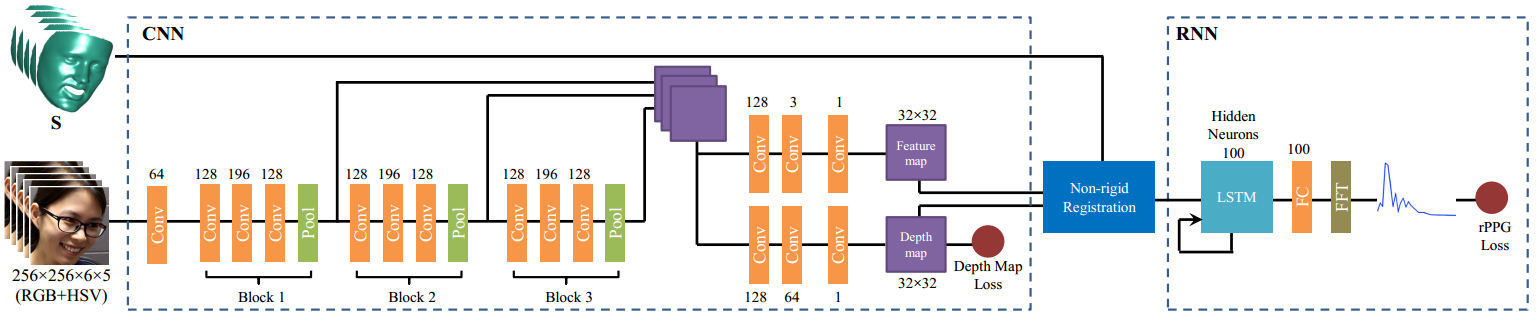
提出的 CNN-RNN 模型一方面使用 pixel-wise 估计人脸深度信息, 另一方面利用时序信息估计 rPPG 信号. 最后, 融合 Depth 和 rPPG 信息进行融合以区分活体和非活体. 文中 CNN-RNN 估计的 rPPG 信号对姿态, 光照和表情有很好的鲁棒性.
亮点:
- short-cut 连接融合了不同尺度信息;
- 非刚性配准处理了估计 rPPG 中的运动和姿态问题.
困难:
- 计算复杂度高
- 未开源, 短期类无法保证研发时间, 风险大
Schemes
算法性能上, 主要考虑 Spatial 和 Temporal 信息. 而空间上可以考虑的 2D 信息和 3D 深度信息.
数据来源上, 主要考虑获取数据源, 单目, 双目或多模态传感器.
模型部署上, 主要考虑算法在平台的运行效率.
综上, 结合嵌入式平台算力, 有如下两种方案可供选择:
Scheme 1
基于 SSD 检测框架, 将活体和非活体当成需要分类的目标进行预测;
Scheme 2
重新设计分类网络:
(1) 数据: 检测人脸向外扩一定比例(如宽/高*0.5), 以提供足够背景信息;
(2) 网络: MobileNet/ShuffleNet/MobileFaceNet 等轻量网络作为 Backbone, 同时融合浅层和深层特征;
(3) 损失函数: Focal loss, Arcface loss 或难样本挖掘技术.
Scheme 3
人脸活体检测和人脸识别网络共享特征层, 构造为 Multi-task Learning 模型.
Open Resources
Open platform
- ArcSoft: http://ai.arcsoft.com.cn/product/liveness_detection.html
- Baidu: https://ai.baidu.com/tech/face/faceliveness
- 华为云: https://support.huaweicloud.com/api-face/face_02_0007.html
- Face++: https://www.faceplusplus.com/face-based-identification/
- 平安云: https://yun.pingan.com/ssr/help/ai/Face/Live
- 阿里云: https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/94323.html
- 腾讯云: https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1030097
- 美团云: https://www.mtyun.com/doc/api/ai/face/LivenessDetection
- 科大讯飞: https://doc.xfyun.cn/rest_api/%E9%9D%99%E9%BB%98%E6%B4%BB%E4%BD%93%E6%A3%80%E6%B5%8B.html
- deepcam: https://www.deepcam.cn/index.php?a=lists&catid=56
Codes
- https://github.com/ee09115/spoofing_detection
- https://github.com/OeslleLucena/FASNet
- hight light removal
- https://github.com/JinghuiZhou/awesome_face_antispoofing
- CNN-for-face-anti-spoofing
- Single Shot Face Anti-spoofing
- https://github.com/senliuy/FaceLivenessDetection (配合式)